
This led to a synthesis of both acceptance and change-acceptingĬlients where they are while pushing for progress and combining a range of change strategies aimed at problem solutions and acceptance strategies with a core emphasis on validation. Therapist humility to see the transactional nature of the enterprise. Radical acceptance by the therapist of the client as is, with slow and episodic rate of progress and the constant risk of suicide, and Spaciousness of the therapist’s mind to “dance” with movement, speed and flow, It became clear was that there was a need for new therapist strategies that could encompass a synthesis of a)Ī technology of change and a technology of acceptance, Clients were equally frustrated by this treatment, saying it was not doing enough to solve their problems. In response, treatment shifted dramatically to focus on warmth and acceptance. Often, clients responded with hostility by lashing out, often at their therapist, or dropping out of treatment altogether.

This focus on problem solving was experienced as extremely invalidating by clients. However, treating such a high-risk and complex population moved the therapists to apply treatment strategies that required clients to make very difficult life changes. Initially, treatment focused on teaching clients effective problem-solving strategies. As a result, the first clinical trials conducted were focused on treating chronically suicidal who also met criteria for borderline personality disorder (BPD), a population known for being at risk for suicide ( Leichsenring, Leibing, Kruse, New, & Leweke, 2011).
#DIALECTIC BEHAVIOR THERAPY MANUAL#
From the beginning the focus of DBT has been to build a “life worth living.” The first complete draft of the treatment manual focused primarily on ameliorating suicidal behaviors however, federal grant funding required that treatment outcome research identify a mental disorder diagnosis.
#DIALECTIC BEHAVIOR THERAPY TRIAL#
In the first randomized controlled trial (RCT), Linehan and colleagues actively recruited the most severe, highly suicidal clients from local area hospitals ( Linehan et al., 1991). In essence, DBT was a trial-and-error clinical effort based on the application of behavioral principles (Bandura, 1969) and social learning theory ( Staats & Staats, 1963 Staats, 1975) to suicidal behaviors ( Linehan, 1981).
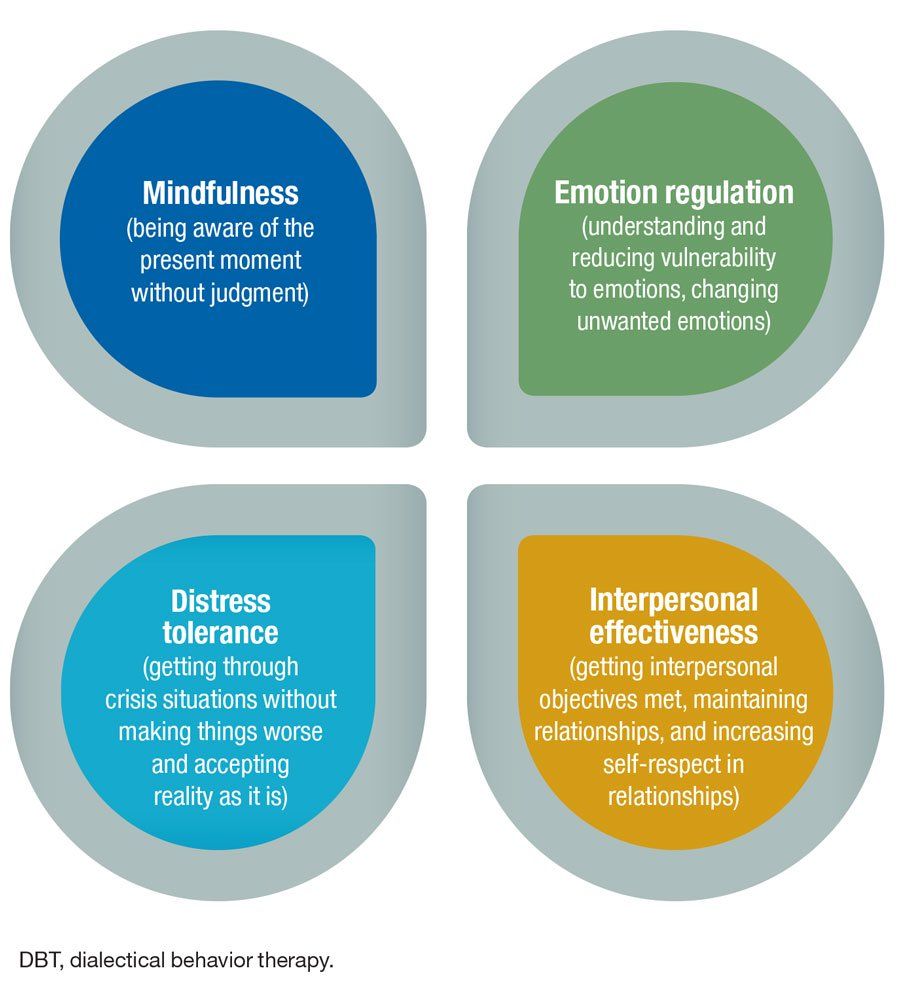
As DBT broadens its reach, the treatment will continue to grow and adapt to meet demands of an evolving clinical landscape.ĭialectical behavior therapy (DBT) emerged from attempts to apply standard behavior therapy to the treatment of highly suicidal individuals. More research is needed to assess how DBT skills work and for whom. There has been an effort to implement DBT skills as a standalone treatment. New skills have been developed and/or modified due to clinical need and/or advancement in research such as treatment outcomes or mechanisms. The inherent modularity and hierarchical structure of DBT has allowed for relative ease in adapting and applying the treatment to other populations and settings.
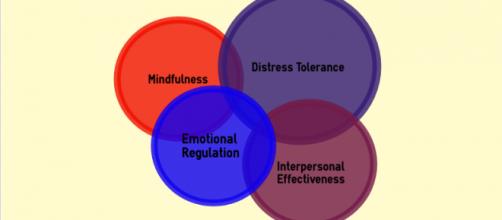
Its development was a trial and error effort driven primarily from clinical experience.ĭialectical behavior therapy is a modular and hierarchical treatment consisting of a combination of individual psychotherapy, group skills, training, telephone coaching, and a therapist consultation team. Dialectical behavior therapy was originally developed from early efforts to apply standard behavior therapy to treat individuals who were highly suicidal.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
